Example Of Implementation Of Concurrent Edrx And Psm
Usage of PSM and eDRX is optional for both NB-IoT and LTE-M. However, research shows that by using these modes in combination can extend the battery life of a IoT device with ranges of up to 10 years for LTE-M and 15 years for NB IoT. This has been enabled by the extended sleep cycles eliminating the unnecessary radio channel activation offered by PSM and longer interval cycle between the paging time windows for eDRX.
What Is The Mcl For Nb
3GPP’s website refers to the book Cellular Internet of Things From Massive Deployments to Critical 5G Applications as a source for more information on Nb-IoT and LTE-M.
According to that book, the MCLs on 4G telecom technology are:
- LTE-M: 160.7 dB
- NB-IoT: 164 dB
On 5G telecom technology, the MCLs for both NB-IoT and LTE-M must be 164 dB.
So, according to those MCLs, NB-IoT and LTE-M have the same penetration depth on 5G. On 4G, LTE-M falls behind the NB-IoT by 3.3 dB , meaning that NB-IoT has a better penetration depth than LTE-M on 4G telecom networks.
Main Nodes For Monitoring And Industrial Automation In Node
The Node-REDs community is more alive than ever, and proof of that are the increasing numbers of available nodes and the number of manufacturing companies that opt for the integration of this software tool. This article will explore the main nodes to develop applications for the industrial automation and monitoring in Node-RED.
Read Also: Terramycin For Cats Side Effects
What Does Research Into Lte
However, prominent companies in the telecom industry have conducted simulations based on the assumptions 3GPP has made. They researched the coverage for LTE-M and its suitability for IoT applications that need deep coverage.
They found that LTE-M has a very similar penetration ability to other LPWA technologies.
LTE-M supports a very similar if not better coverage enhancement compared to other LPWA technologies Gus Vos, Chief Engineer, Technology Standards, Sierra Wireless.
Why? It turns out the assumptions underlying 3GPPs MCL calculations varied between technologies and thus was not a fair comparison.
These are the numbers used for calculating the MCL for LTE-M and NB-IoT in 3GPP standards:
| 5 dB | 3 dB |
3GPP 36.888 and 3GPP 45.820 reveal the numbers are based on different transmit power, noise figure, and target throughput assumptions.
They went deep on the MCL calculations using typical LTE-M assumptions for the receiver noise figure and transmit power and found the penetration for LTE-M to be identical or better than NB-IoT.
What Is Lte Cat M1 Device Connectivity
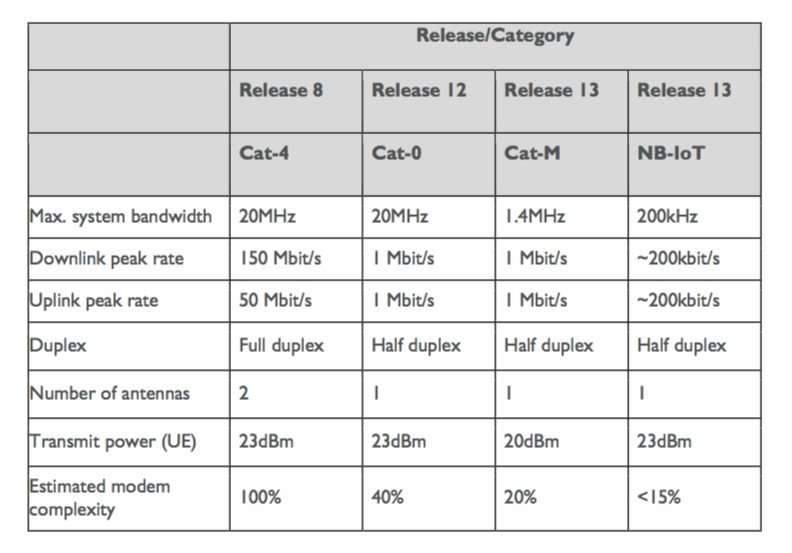
LTE CAT M1 also known as LTE-M is an LPWAN cellular technology that specializes in transferring low to medium amounts of data across a wide geographical range.
With low power requirements LTE CAT M1 is an energy efficient solution that maximizes the uptime of your deployed IoT devices. This extended battery makes it one of the more cost-effective connectivity solutions. It lessens the frequency with which batteries need to be replaced across an entire deployment, reducing human capital requirements and limiting costly downtime. When the devices are not actively sending or receiving data, CAT M1 even enters a power-saving mode that improves operational efficiency while reducing resource waste.
LTE CAT M1 also cuts costs thanks to its reliance on existing LTE infrastructure, which eliminates the need to build antennas and other network necessities to support IoT connectivity. CAT M1 modems also require less power to operate, making them cheaper to maintain in the long term.
Don’t Miss: Pine Litter Scoop
What Are The Differences Between Lte Cat M1 And Nb
Cody LiretteCAT M1Cellular ConnectivityIoTNB-IoT
With some experts predicting that there will be more than 41 billion IoT devices in circulation by 2027, its clear that businesses and developers are investing in IoT as an important part of their future.
As such, developers are searching for IoT device connectivity that can support the specific coverage, availability, features, and price point that they need to successfully bring their ideas to market.
Choosing the right connectivity technology for your business is essential. There are numerous factors that can impact that decision, from something as simple as the location of the deployment to the complexities of scaling. The right connectivity can improve quality of service, cut costs, and strengthen operational efficiency, creating a competitive advantage that allows businesses to innovate more readily.
With the seemingly endless string of acronyms that come with the IoT space, it can be difficult to differentiate one IoT connectivity solution from the next. This is particularly true when the project requires a low-power wide-area network , the two most prominent cellular forms of which are LTE CAT M1 and NB-IoT.
To help you make the correct decision for your deployment, here are the differences between LTE CAT M1 and NB-IoT.
Iot Applications Have Several Requirements That Are Not Ideally Met By 2g 3g Or Previous Lte Modems
- Unlike traditional cellular applications, IoT devices tend to transmit small, often infrequent bursts of data.
- IoT applications often operate in remote, temporary, or mobile locations, where they rely on off-grid power. And because they are usually unattended they may have to rely on backup battery power for some time if grid power fails. For these reasons, IoT modems need to draw as little power as possible, both in use and in standby modes.
- IoT applications tend to require large numbers of nodes, so modem cost can be a significant issue. The ideal IoT modem costs much less than a traditional cellular modem.
Both LTE Cat M1 and NB-IoT were created by the 3GPP standards body in Release 13 to meet these specific requirements. The most obvious difference is that LTE Cat M1 is available today, while NB-IoT is approaching availability in Europe and Asia and still a year-and-a-half or more away from availability in the US.
Similarities
Both Cat M1 and NB-IoT will operate on licensed spectrum, which provides excellent security and quality of service. They will both provide better access in challenging sites like buildings than some of the earlier cellular service options, due to the reduced channel sizes and features like coverage enhancement modes . Both can take advantage of power saving mode , in which the device can, when not actively communicating over the network, go into deep sleep mode for long periods of time while keeping time and storing data in flash memory.
Recommended Reading: What Was Hp Lovecraft’s Cats Name
Preparing For 5g Lte Cat M Vs Lte Cat Nb
Digital acceleration continues unabated with the global pandemic further hastening the focus and urgency for organisations in ensuring that they have total visibility of their assets. This quickening has been further supported by the role out of 5G which although in the early stages of commercialization promises higher bandwidth, enhanced reliability and lower latency. Collectively this is referred to as QoS and is indeed needed for the next generation of IoT devices driving the digital transformation. With 2G / GSM and 3G / UMTS networks now starting to be phased out, network technologies in the form of LTE Cat M and LTE Cat NB-IoT will increasingly support LPWAN in enabling global mass IoT connectivity.
Even though 5G has been available since July 2019 availability has been slow to come online when compared with the equivalent coverage offered by 2G/3G and LTE. The impact in speed of deployment resulting from the smaller cell sizes and larger overall infrastructure required for the new technologies when compared to that deployed for previous standards.
The spectrums within 5G can be broken down into three categories, namely
- Sub-GHz.
- 1 6 GHz.
- High band mmWave.
LTE Cat M vs. LTE Cat NB-IoT Selection Criteria
LTE Cat M vs. LTE Cat NB-IoT Optimal Performance
What Are The Cat M1 Vs Nb
LTE CAT M1 uses the existing LTE network for operation, but unlike NB-IoT, LTE CAT M1 operates in the same LTE frequency band used in cellular applications.
One of its advantages is that it has the ability to switch from one cell site to another, which makes it possible to use the technology in mobile applications
However, NB-IoT does not allow mobile handover from one cell site to another cell site, so it can only be used for fixed applications, that is, applications limited to the area covered by a single cell site.
Because LTE Cat M1 technology can coexist with 2G, 3G, and 4G mobile networks, it has all the advantages of mobile network security and privacy features, such as supporting user identity confidentiality, entity authentication, confidentiality, data integrity, and mobile devices The function of identification, etc.
The latest LTE CAT M1 specification was approved in June 2016 in the version 13 agreement of the 3GPP specification . According to the definition of Release 13, the technical specifications of LTE CAT M1 are as follows.
Deployment: LTE frequency band in-band
Downlink peak data rate: 1 Mbps
Uplink peak data rate: 1 Mbps
Delay time: 10-15 ms
Don’t Miss: How To Make Forest Little Alchemy
For Other Field Tests That Were Carried Out For Data Delivery Times And Battery Life The Results Are Shown Here
Features
New timers have been introduced to optimise the performance of IoT devices utilising these LPWA technologies. Two of these are Power Save Mode and extended Discontinuous Reception released in 3GPP Rel12 and Rel13 respectively.
In PSM the UE would maintain its pdp context , also known an PDN connection, with the EPC , but its radio or antenna would be powered down. This leads to a difficulty in paging the IoT device to receive MT traffic, leading to loss of packets as a local Serving Gateway
would only keep packets for previously configured amount of time in its queue before these packets get discarded. So why use PSM? The benefits are based on the fact that an IoT device would be using less power as it is in a power saving state and this increases the longevity of an IoT device powered by a DC battery.
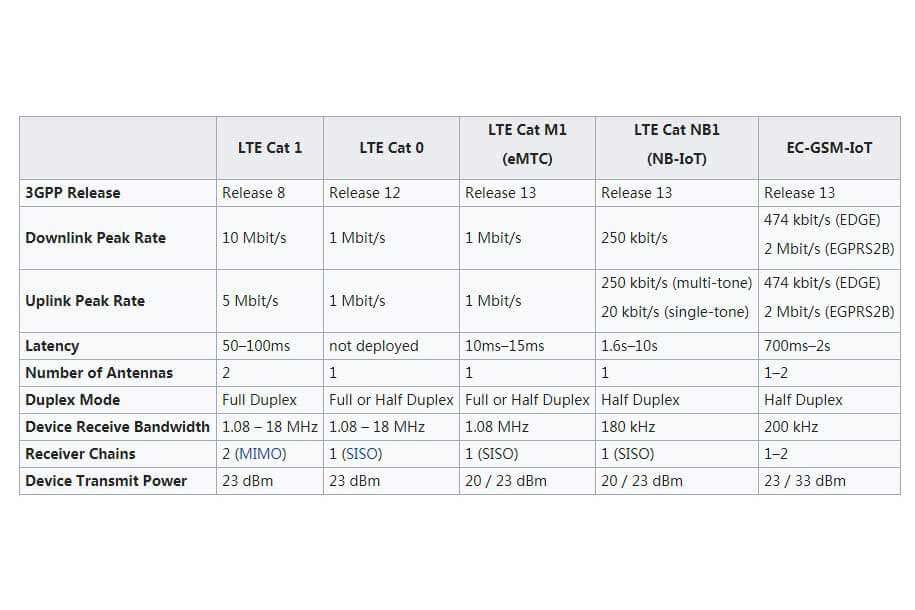
Technical Comparison There Are Various Differences Between Nb
One of the main features concerning LPWA technologies is the enhanced coverage capability for LTE-M the Maximum Coupling Loss has an additional gain of approximately 10dB and 20dB for NB-IoT when compared to GSM.
This is achieved by a few factors:
- Repetition of transmissions
- New control channels
- Size of UE bandwidth
Read Also: How Old In Cat Years
New Emanager Modules Integrated With Node
As we announced in previous blog entries, we are performing a full integration between eManager and Node-RED software, creating customized nodes for each of our expansion modules. Today we present two new modules which are already integrated in Node-RED: the module of 5 Digital inputs and 2 Power relays and the Supercap module.
Data Rate And Latency
LTE-M boasts the highest bandwidth and data rate of all existing LPWAN technologies, which is particularly relevant if you are looking for the flexibility to upgrade device capabilities along the line. The maximum data rate of LTE-M is higher than NB-IoT by orders of magnitude, making the former the only option for mission-critical applications that requires millisecond latency.
Whats more, even if a low data rate is sufficient for your use case today, will this change over the next few years as your IoT solution evolves and new customer requirements come into play? Changing the connectivity module, later on, is not only cost- and labor-intensive but also requires re-certification of devices.
Having a long-term view in terms of bandwidth requirement will help future-proof your solution with an informed connectivity decision.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Cat’s Name On The Smurfs
The Reality And Current Limitations Of Lpwan
Low-power wide-area technology is relatively new. Therefore, it is important to know the current situation and future prospects. For IoT deployment, the most critical aspect is global availability.
The GSMA has a handy resource called the Mobile IoT Deployment Map. You can see the global deployment of NB-IoT and LTE-M technologies in it.
According to the latest figures, there are 162 LPWAN networks worldwide. Two-thirds of them are NB-IoT networks, and the remaining 55 are LTE-M. In case of interest of availability in a specific country, I would suggest you look it up yourself. Right now, LPWAN networks exist in 62 countries.
Unfortunately, due to the lack of roaming agreements between telecom companies, your devices cannot travel from one country to another and roam freely.
If you are using your devices in multiple countries or moving from one country to another, you need to be aware of the nuances of roaming with LTE-M and NB-IoT.
If your devices are stationary and you know where they will be deployed, NB-IoT or LTE-M may be a viable option for you.
That said, NB-IoT and LTE-M are in their infancy, and it’s currently helpful to have 2G or 4G fallback options.
But let’s take a closer look at each technology to understand how they differ and what they are best suited for.
The Value Of Intelligent Iot Connectivity
As the world continues to embrace Iot in everything from driverless cars and smart cities to predictive business indexes and fleet management, its clear that choosing the correct IoT connectivity for a deployment will be an integral part of many businesses agendas.
IoT cellular connectivity whether LTE CAT M1, NB-IoT, or others can provide tremendous value to a project. Though there are many variables to consider when choosing the right IoT connectivity to meet your specific needs, working with a nuanced connectivity provider that goes beyond cellular technologies can be a game changer.
Let Soracom help power your IoT project with a blended network solution that provides the most coverage and uptime at the greatest price point.
Weve helped over 20,000 businesses drive their IoT dreams to reality with a powerful unified management platform that allows users to mix multiple connectivity technologies into any deployment. Being able to function on a combination of cellular, WiFi, Ethernet and even satellite connections offers a considerable flexibility for developers at a fraction of the cost of competitors.
Our expert team is ready and willing to answer any questions that you may have about your IoT project, providing you with the information and resources that you need to take your business to the next level.
Editors Note: This post was originally published in August 2019 and has been updated for accuracy.
Don’t Miss: Long Hair Calico
Global Deployment And Roaming Conclusion
The decisions here depend on where your device will be situated and whether or not it will need roaming. If your device might need to roam, LTE-M is your natural choice.
If your device will be static in, e.g. China, then NB-IoT is currently the choice that makes sense.
Nevertheless, NB-IoT and LTE-M are still in their early days, and its currently helpful to have 2G or 4G fallback options, for example.
Using Edge Computing And Node
It is relatively easy to put together an IoT proof of concept that sends device data to the cloud, but the challenges get more complex when deploying enterprise-grade IoT at scale. These challenges include integration with factory and enterprise systems, data securitization and doing all of this without incrementing the project budget. Check how Node-RED and Edge computing can help on IoT company projects.
Recommended Reading: How Many Years In Cat Years
What Is Lte Cat M1
LTE Cat M1 is a new low-power wide-area cellular technology specially designed for Internet of Things and machine-to-machine communications. It has been developed to support low to medium data rate applications with upload/download data rates below 1Mbps and can be used in half-duplex or full-duplex mode.
National And Global Roaming
Both LTE-M and NB-IoT are relatively new technologies where dedicated roaming agreements have not yet been widely in place among network operators. However, due to its technical configuration, LTE-M roaming is, in practice, possible over traditional 4G infrastructure. For example, using EMnifys IoT SIM, LTE-M modems can piggyback on our existing national and global 4G roaming to get multi-network LTE-M access in 45 countries . This brings two important benefits for IoT businesses:
- Improved coverage and service availability within a country
- Reduced complexity with a single SIM for cross-border network service
On the other hand, NB-IoT roaming largely depends on official agreements between network operators, which are still very limited. Multiple reasons come into play, one of which is that operators have yet to work out their NB-IoT charging model among each other. Also, features like Power Save Mode and Extended Discontinuous Reception have not been consistently deployed, causing roaming difficulty when, for example, a device moves from a network with PSM to one where PSM is not available.
Due to limited NB-IoT roaming, you likely need separate operator contracts and SIMs if devices are distributed globally and are bound to one operators service within each country.
You May Like: How Long After A Cat Stops Eating Will It Die
Example Of Implementation Of Psm
To address the loss of packets, eDRX was introduced. This allowed for more successful delivery attempts of MT traffic while providing support for MO traffic. When a device utilises eDRX, it allows the device to be paged while it is in idle state utilising a paging transmission window to allow for a paging occasion .
Introduction To The New Network Technologies Lte
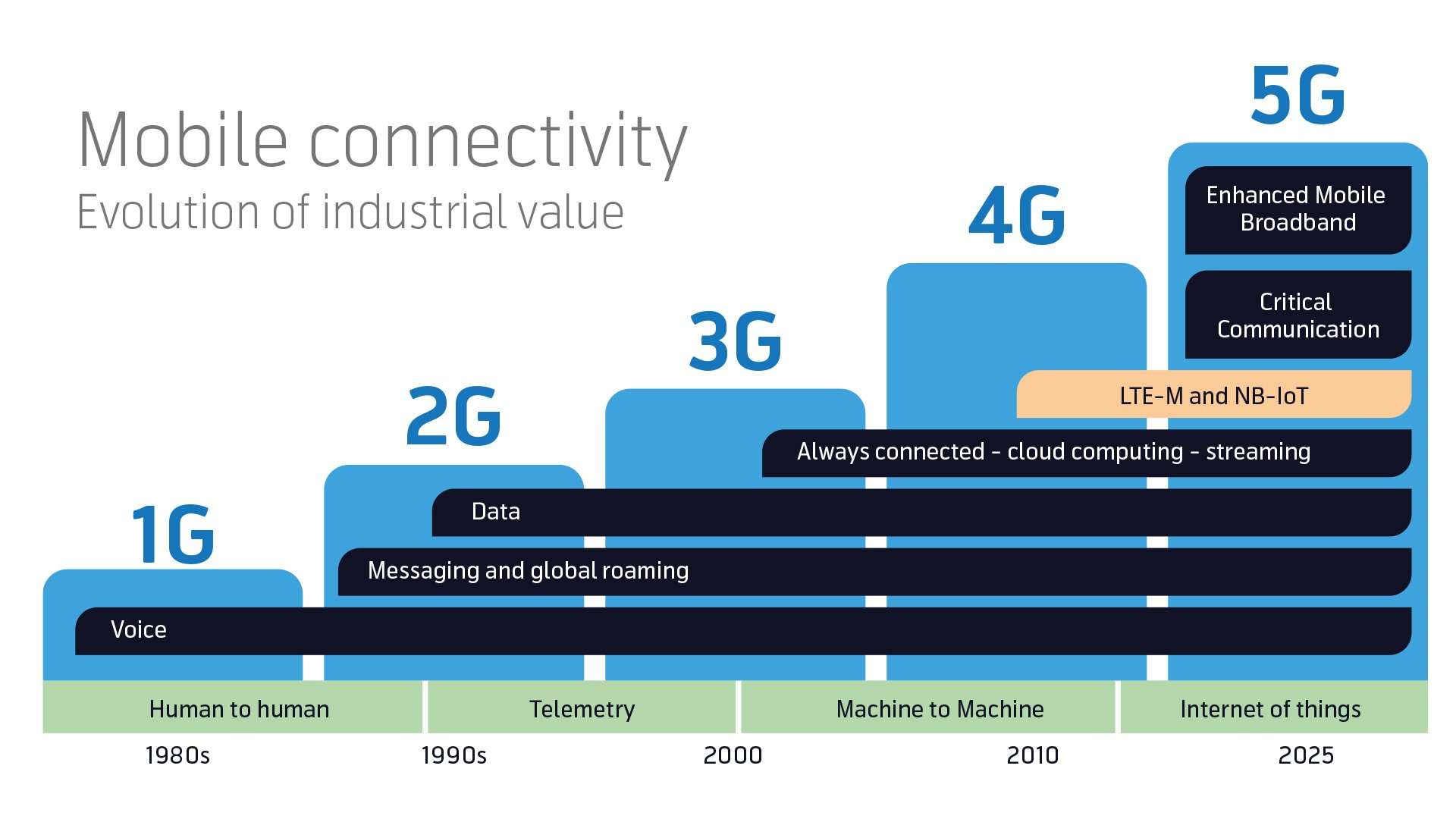
Two new network technologies, both based on mobile technology, are entering the market in the form of LTE-M and NB-IoT both created to be particularly suitable for enabling global IoT connectivity.
LTE-M and NB-IoT are both good connectivity options for industries looking to take advantage of LPWAN technology, that enhances the battery life of devices and connects devices that have previously been hard to reach. They are both available today, standardized and built on the 4G network which means they are future-proof, have global network coverage and are backed up by GSMA and telecom standards.
Connectivity is a crucial part of product design and performance and the choice of connectivity technology must be considered early in the process. This is a challenging choice given the quick technology and market development. 5G technologies are around the corner, 2G and 3G networks are starting to be phased out and new network technologies that support LPWAN are starting to become globally available in the form of LTE-M and NB-IoT also referred to as Mobile IoT.
For the first time networks have been developed to answer to the specific needs of connecting things. Previously, connected units have been communicating on infrastructure developed for consumer needs.
LTE-M and NB-IoT will be the obvious choices for industries looking for 2G and 3G replacements for devices with long lifecycles, requiring extended device battery life and coverage.
You May Like: Cats In Human Years